Describe How New Viruses Are Produced in the Host Cell
The cell uses its own resources to build copies. Uses the host cell organelles to make new capsids which are coded for on its DNA 4.
Virus Infections And Hosts Boundless Biology
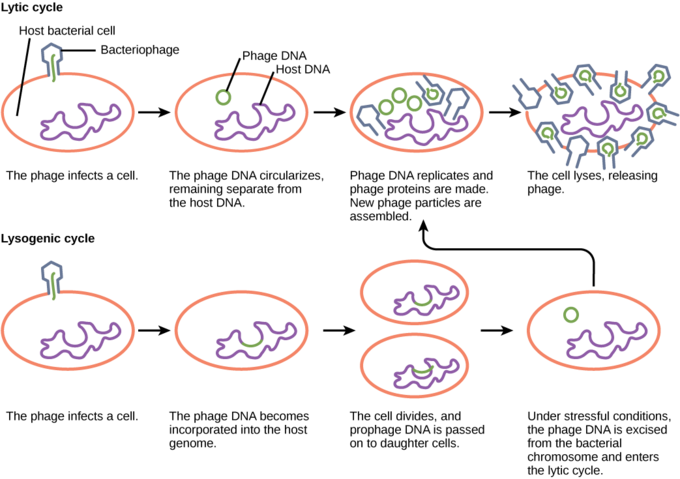
In the lytic cycle the virus attaches to the host cell and injects its DNA.
. As viruses are obligate intracellular pathogens they cannot replicate without the machinery and metabolism of a host cell. Virus replication requires specific interactions with host cells. Of course there are exceptions to this pattern.
Following this the virus is engulfed. The other viruses follow the process called exocytosis where the virus exits from the cells own pathways. As a result the virus is engulfed.
Interferons prevent replication of viruses by directly. Assembly viruses are produced from the viral components. The replication cycle begins with attachment of viral proteins to host cell receptors.
Viruses replicate within a living host cell producing changes in the cell that often result in the death of the infected cell. RNA and proteins are then made and assembled into new virions. Synthesis the viral proteins and nucleic acid copies are manufactured by the cells machinery.
In this way the virus. Viruses may have genes but they contain no cell parts and are not made up of cells. RNA and proteins are made and assembled into new virions.
Viruses cause a lot of diseases. When viruses invade a bodys cells and begin to multiply they make the host sick. The cell makes so many copies of the virus that it can cause the cell membrane to rupture explode lyse.
The viral surface molecule can be likened to a. In influenza virus infection glycoproteins on the capsid attach to a host epithelial cell. Viruses have proteins on their surface that typically latch onto a specific molecule on the surface of a host cell called a receptor.
It degrades the host DNA through hydrolysis 3. Although the replicative life cycle of viruses differs greatly between. The DNA also codes for.
Virally infected cells produce and release small proteins called interferons which play a role in immune protection against viruses. Thus viruses are considered intracellular parasites. Instead they depend on a host cell to reproduce.
The presence or absence. As the new virion buds out from an infected host cell it is wrapped by the cells bilayer membrane and carries with it any protein that happens to be embedded in the. Some follow the process called lysis where the virus bursts the host cell.
They do not require energy and they do not take in food or give off waste products. New viruses can also emerge through genetic mutations within the virus genome which are more common among viruses that instead of DNA store their genetic information in. Upon entrance into the host cell the plus-strand RNAs generated by the polymerase are used as mRNA for protein production.
Release newly formed virions. After entering the body in the case of coronavirus this occurs through the nose mouth or eyes a virus attaches itself to a host cell. When viral genomes are needed the plus-strand RNAs are used.
A bacterial virus infects the cell by attaching fibers of its protein tail to a specific receptor site on the bacterial cell wall and then injecting the nucleic acid into the host leaving the empty capsid. The viral mRNA directs the host cell to synthesize viral enzymes and capsid proteins and assemble new virions. Viruses replicate within a living host cell producing changes in the cell that often result in the death of the infected cell.
In influenza virus infection glycoproteins attach to a host epithelial cell. It becomes an unwitting pawn. Virus injects it genetic material 2.
Thus viruses are considered intracellular parasites. Using the hosts cellular metabolism the viral DNA begins to replicate and form proteins. It becomes an unwitting pawn in the viruss sick game the lytic phase.
The virus can use either the outer membrane of the host cell or an internal membrane such as the nuclear membrane or endoplasmic reticulum.

The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology

Virus Infections And Hosts Boundless Biology

Diagram Of The Viral Life Cycle A Virions Bind To Host Cell Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Describe How New Viruses Are Produced in the Host Cell"
Post a Comment